Contenido principal
Features
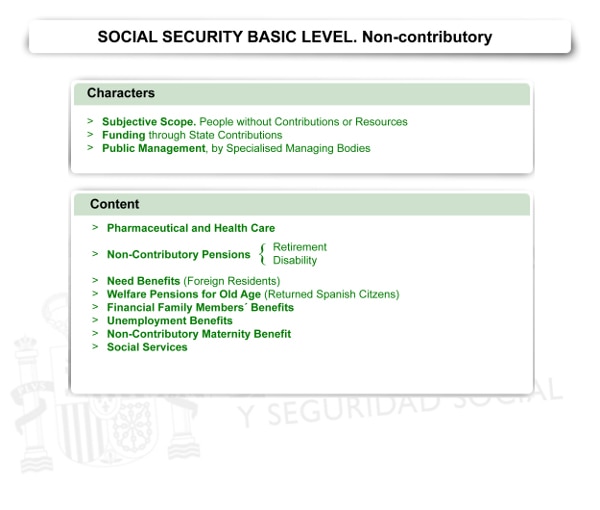
Protection through non-contributory benefits, to a greater or lesser extent, started to shape itself after the 1980s, when the government started a slow progressive reform to the Social Security System. The main features of this reform were:
- Scope of individuals, which refers to the inclusion in the System´s scope of application of all the people who, for whatever reason, have never made any contributions or made insufficient contributions to be entitled to its benefits, and do not have sufficient resources to maintain a minimum standard of living.
- Funding, manifested in the benefits payable by the General State Budget, given that it is a model that assumes the existence of a legal relationship of direct protection between the state and the protected individuals, which they are not as individuals of an employment relationship or self-employed activity.
- Management, of a public nature, which is exactly the same as with the contributory level and it is also carried out by specialist Managing Bodies:
- The management of retirement and disability pensions corresponds to the Managing Body of the Social Security System which also has responsibilities relating to supplementary benefits, the Institute for the Elderly and Social Services (IMSERSO) or the competent bodies of the Autonomous Communities to which management duties and services have been transferred.
- The management and granting of financial benefits for family protection is carried out by the National Institute of the Social Security (INSS).
- The implementation of the health care benefit is done by the competent service of the Autonomous Communities or the National Health Care Institute (INGESA) in the cities of Ceuta and Melilla.
- The management of the unemployment or welfare benefit is carried out by the Public State Employment Service.
Currently, the IMSERSO and the INSALUD (INGESA) have transferred their responsibilities to all of the Autonomous Communities, except in the cities of Ceuta and Melilla.